
The author introduces the concept of "hard cutting" for efficient machining of high-hardness materials from the improvement direction of workpiece materials brought about by the trend of lightweighting in the automotive industry, and introduces its application and development direction.
1. The trend of lightweight parts materials
With the rapid development of the automobile industry, higher and higher requirements are placed on the engine, and the engine is gradually developing in the direction of high power, low energy consumption and long service life.
One of the important trends is the all-aluminum engine.

As the last brilliance of traditional engines before the advent of new energy vehicles, mainstream car brands currently have their own all-aluminum engine series. To a certain extent, the all-aluminum engine has also become one of the symbols that distinguish the old and new engines.
Although an all-aluminum engine—mainly an aluminum block—can reduce the overall mass of the engine, aluminum’s low wear resistance and high coefficient of thermal expansion make it necessary to choose other materials for parts that are in frictional contact.
Take the valve seat as an example
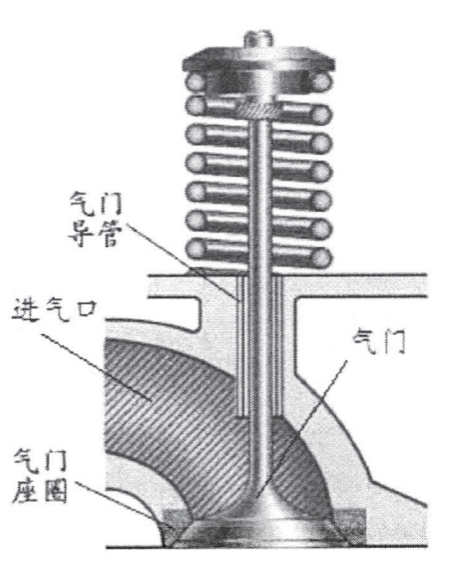
As an important part of the engine, the performance of the valve seat affects the overall performance of the engine, which prompts people to continuously research and develop new materials for the valve seat, and use miniaturized, automated, and sophisticated equipment as much as possible. material preparation method.

At present, domestic and foreign valve seat materials can be summarized into two categories. One is traditional materials based on metals and their alloys; the other is non-traditional materials represented by new materials such as ceramic materials.
The preparation process of valve seat ring of metal alloy material mainly includes casting and powder metallurgy forming process. However, due to the high rejection rate and low product precision of the cast valve seat, and with the popularization and use of low-lead or unleaded gasoline, the surface self-lubrication of the valve seat is reduced, and the wear is sharply increased. The powder metallurgy valve seat ring has better self-lubricating effect and less chips during processing, so it is widely used.
Powder metallurgy technology is a metal forming technology that uses metal powder (or a mixture of metal powder and non-metal powder) as the basic raw material, after forming and sintering, to prepare metal alloy materials.
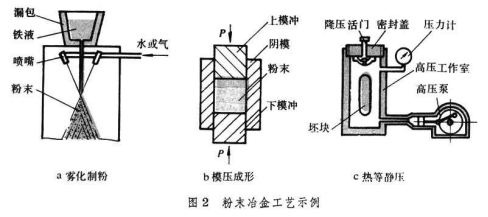
Compared with the traditional casting technology, the material properties of the valve seat formed by powder metallurgy have been significantly improved, with unique self-lubricating friction reduction, more complex shape and richer material functions. Powder metallurgy technology is not only a manufacturing process of high-strength, high-density, complex shape, no cutting, and less cutting parts, but also a processing method for producing new materials. Nowadays, powder metallurgy materials are widely used and develop rapidly.
Although the powder metallurgy forming process aims to eliminate all processing and direct forming, the current powder metallurgy technology cannot ensure that the product size meets the accuracy requirements. Powder metallurgy valve seat parts are only close to their final shape and require cutting finishing.
However, due to the high hardness of powder metallurgy materials after pressing and sintering, ordinary cemented carbide tools are difficult to process, and due to the unique porosity of powder metallurgy materials, the cutting tool wear is large and the tool durability is low, which greatly affects the processing. effectiveness. Therefore, the machining of powder metallurgy valve seat puts forward higher requirements for tool materials.
2. Overview of hard cutting technology
Hard cutting refers to the direct cutting of high-hardness materials with hardness greater than HRC50. The workpiece processing quality is good, the dimensional accuracy of the workpiece can be controlled within 3μm, and the surface roughness Ra can reach 0.2-0.4μm. Therefore, it is generally used as a part. The final finishing operation.
Compared with grinding, hard cutting has the following characteristics:
1. Good processing flexibility and low cost.
Compared with grinding, hard cutting uses single-point cutting of turning tools. When machining workpieces with complex shapes, it is only necessary to change the shape of the cutting edge and the way of cutting, which breaks through the limitations of grinding wheel grinding and reduces workpiece handling and re-processing. Clamping time.
2. Less investment in equipment.
Hard cutting can be carried out directly on the existing lathe without special tools or special grinders, while grinding requires special grinders.
3. In line with the concept of green manufacturing.
Grinding produces a large amount of waste grinding fluid, which is difficult to handle and remove, while hard cutting does not require cutting fluid and has low energy consumption.
At present, the new process of hard cutting has been more and more widely used in machining, and has gradually become the preferred process to replace grinding.
For example, in the automobile manufacturing industry, this method is used for semi-finishing and finishing of certain parts such as transmission shafts, gearboxes and engines, reducing the investment of some special machine tools and reducing equipment costs; hardened steel materials in the mold industry Using hard cutting technology instead of grinding or EDM will greatly reduce the polishing workload of mold finishing and shorten the development cycle of molds.
1. Development direction of hard cutting
It is precisely because the hard cutting technology has a good development prospect that scholars from all over the world have invested a lot of energy in research.
In foreign countries, the research on hard cutting technology is more mature. Some foreign research institutions combine the cutting test results with computer simulation and finite element simulation technology, which makes the hard cutting technology develop by leaps and bounds.
Today, hard cutting technology is widely used in automobile manufacturing, bearing industry and industries of various difficult-to-machine materials, and has produced huge economic benefits.
Y. Kevin Chou and Chris J. Evans of the United States used the BN series PCBN tools of Sumitomo Corporation to process AISIM50 steel, realizing the nano-level machining accuracy of PCBN tools for machining hardened steel.
The German Chmalkalden company can make the surface roughness of the machined stable to reach the grinding quality level (Ra=3μm) on the ordinary CNC machine tool. 55% of the applications of Japanese PCBN tools use hard cutting to replace the original grinding.
Domestic scholars have also invested a lot of research on hard cutting technology, and have done a lot of work on tool wear and machined surface quality during hard cutting. Through experimental research, it was found that the hardness of the material to be processed affects the cutting force, cutting temperature, surface quality and other indicators, and the concept of critical hardness was put forward.
In addition, hard cutting technology is gradually accepted by enterprises for its cost-saving and high-efficiency characteristics, and is gradually widely used in domestic machining. For example, a gear manufacturing company uses PCBN tools and ceramic tools to turn 22CrMoH gears. Once clamping, the processing process is completed within 5 minutes, and a good surface roughness is obtained. Compared with the original grinding process that takes 12 minutes, it is greatly Improve production efficiency; China First Heavy Group adopts PCBN tools for high-speed cutting of hardened steel support rollers, which improves processing efficiency and reduces tool wear costs.
【Summary of the article】
In this article, the author briefly introduces the concept of hard cutting and its development direction. In the next issue, we will introduce the most suitable tool material for hard cutting - PCBN tool. How to play the cost-effectiveness of PCBN tool in hard cutting? Can PCBN be wet cut? The next article will be interpreted by readers.
References: Ye Zheng, "Research on the Hard Cutting Performance of PCBN Tool Negative Chamfering".